Nerve Pain Treatment in Jersey City
Nerve Entrapment Disorders:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Repetitive work can cause pressure on the median nerve in locations other than the wrist and can also affect other nerves in the arm and hand.
Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome: The ulnar nerve supplies sensation to the ring and little fingers. Like the median nerve, it too can become trapped as a result of repetitive stress, with subsequent loss of sensation in these fingers and the outer half of the palm. This condition, known as ulnar tunnel syndrome.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Pinched nerves in the neck may also cause weakness in the hands. A disorder known as thoracic outlet syndrome caused by compression of nerves and blood vessels running down the neck into the arm can cause symptoms very similar to CTS. The compression occurs at the first rib in the front of the shoulder.
Diagnosis:
- Electromyography
- Nerve conduction velocity studies
- Thermography
Electrodiagnostic Tests:
There are two common types of electrodiagnostic tests: nerve conduction studies and electromyographies. The tests analyze the electric waveforms of nerves and muscles to detect median nerve compression in the carpal tunnel. To perform nerve conduction studies, surface electrodes are first fastened to the hand and wrist. Small electric shocks are then applied to the nerves in the fingers, wrist, and forearm to measure the speed of conduction of sensory and motor nerve fibers. To perform electromyography, a fine sterile, wire electrode is inserted briefly into a muscle and the electrical activity is displayed on a viewing screen.
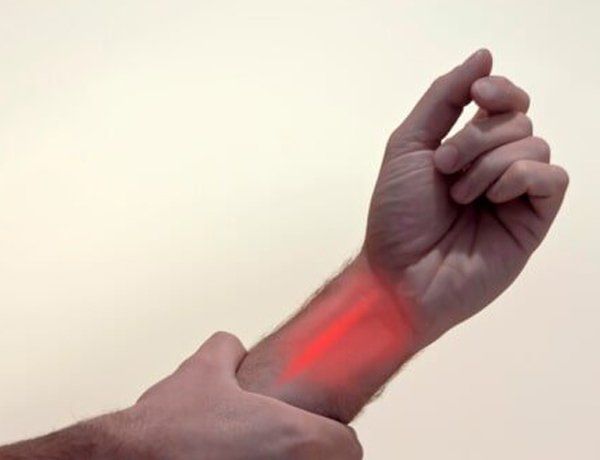
Tingling
Tingling is an indication of damage or irritation to the nerves in that area. Unlike numbness, tingling suggests the nerve is not completely dead or severed, just injured or experiencing pressure.
Common Causes:
- Local injury to the nerves under the skin
- Lack of blood supply to the area
- Pressure on the nerves, caused by a herniated disk, tumors, abscesses or arthritic bones
- Toxic action on nerves (lead, alcohol, tobacco)
- Diabetes and other chemical abnormalities
- Vitamin B-12 deficiency
- Hypothyroidism
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Drugs such as chemotherapeutic agents, chloroquine, D-penicillamine, isoniazid, nitrofurantoin, parenteral gold therapy and phenytoin
- Long-term radiation
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis (a less common cause of numbness)
There may be other causes of numbness. This list is not all inclusive. Call your health care provider if:
- Tingling or numbness is not explained by an obvious cause (such as position-related "falling asleep" of a hand or foot).
- Numbness and tingling is accompanied by other symptoms.
- Numbness and tingling lasts longer than a few minutes.
Please explain to your physician the:
- Quality of the pain.
- Radiation of the pain.
- Site of the pain.
- Time of the Pain.
Diagnostic Tests:
Diagnostic tests that may be performed include:
- Blood tests (such as CBC or blood differential)
- CT scan of the head or affected area
- Electromyography
- Myelography
- X-ray of the head or affected area
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the median nerve at the wrist.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is predominantly caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist due to hypertrophy or edema of the flexor synovium.
Sex: Prevalent in females.
Age: Middle-aged persons.
History:
Sometimes, patients complain of an intermittent pins-and-needles sensation in the median nerve distribution of the hand. This kind of sensation is generally worse at night.
- Common symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome are most often bilateral, insidious in onset and progressive in nature.
- With advanced nerve compression, the aching sensation is persistent and static and may radiate to the forearm and elbow.
Physical:
Tapping the volar wrist over the median nerve (Tinel's sign) may produce paresthesias in the median distribution of the hand.
- Thenar atrophy may be present in advanced cases of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
- Hyperflexion of the wrist for 60 seconds may also elicit paresthesias (Phalen's sign).
Causes:
- Activities involving repetitive wrist flexion, such as assembly packing, computer keyboard work, playing a musical instrument and craftwork, can cause inflammation of the flexor tendon sheath.
- Pregnancy or oral contraceptive-related related edema can cause compression of the median nerve.
- Trauma of any type, including fractures, can cause edema that can compress the median nerve.
- Tuberculosis
- Hemodialysis
- Hypothyroidism
- Amyloidosis
- Acromegaly
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Renal failure, diabetes mellitus and obesity have all been associated with an increased risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Imaging Studies:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is reasonably accurate in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Electromyographic (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies:
- EMG and nerve conduction studies help to confirm the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- They are most helpful in the determination of the site and severity of nerve compression.
Treatment:
- Medicine and rehabilitation mesaures.
- Splinting
- Injection (steriod)
- Surgical interventions
Facial Paralysis
Definition:
Total loss of voluntary muscle movement of one side of the face.
Alternative Names:
Bell's Palsy
Treatment:
- Physical medicine and rehabilitation measures
- Medications
- In rare cases depending upon the cause -> surgical intervention